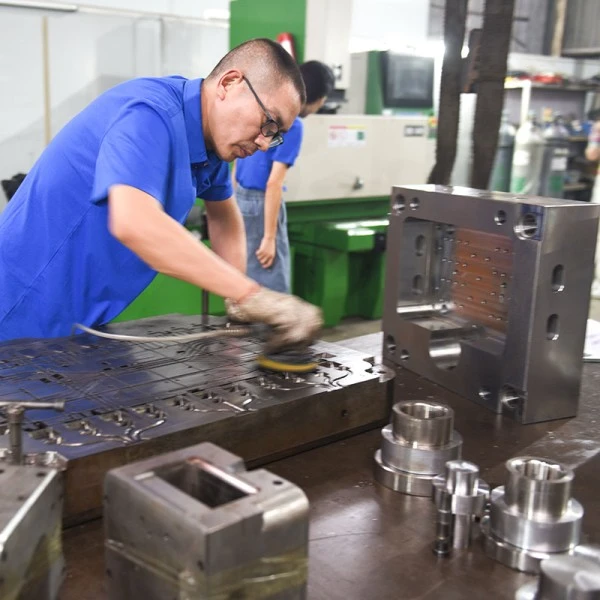
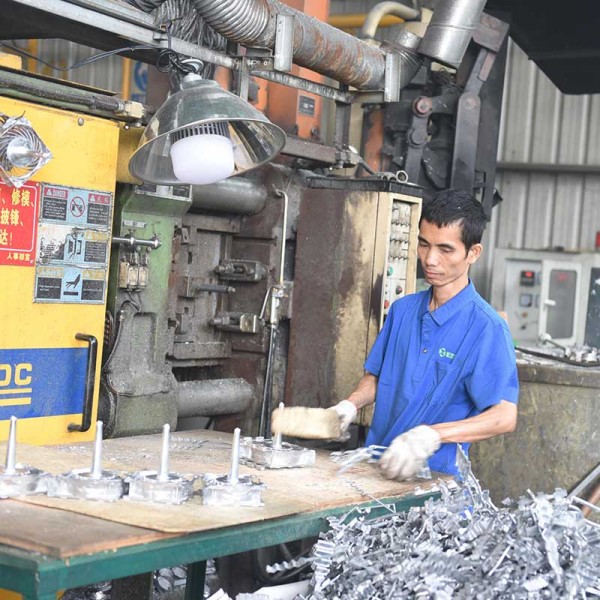
In our daily lives, we can come into contact with a wide variety of products, including those made of plastic, zinc alloy, aluminum alloy, and even magnesium alloy. Have you ever seriously considered a question: Why are these products made of these materials? What types of materials are most suitable for producing which products? Well, let’s have a brief discussion today. What are the differences between aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy materials? And what kind of products are they more suitable for?
I. Density
The density of aluminum alloy is relatively large, usually around 2.7g/cm³. The commonly used aluminum alloy for conventional die casting, ADC12, has this density. Due to this relatively high density, aluminum alloy die castings generally weigh more. Compared with aluminum alloy, the density of magnesium alloy is smaller, usually ranging from 1.7 to 1.9g/cm³. The commonly used magnesium alloy material, AZ91D, has a density of about 1.8g/cm³. This makes magnesium alloy die castings lighter than aluminum alloy die castings of the same volume. It can be seen that magnesium alloy has an advantage over aluminum alloy in certain products that require strict weight reduction.
II. Cost
The material cost of aluminum alloy is relatively stable, usually around 21 yuan/kg. The sources of its raw materials are relatively extensive, and the recycling utilization rate of aluminum alloy scraps is relatively high, so its price fluctuation is relatively small. In contrast, the material cost of magnesium alloy is relatively high, with larger losses, usually ranging from 23 yuan/kg to 26 yuan/kg. Because the refining process of magnesium is relatively complex, and magnesium alloys are prone to catching fire during the production process, significant losses may occur, which increase the cost to a certain extent.
III. Application Fields
Aluminum alloy products are primarily used in components such as automobile engine blocks, transmission housings, and radiators, mainly meeting the performance requirements of high strength and thermal stability. Magnesium alloy is generally applied in the field of thin and light 3C products, such as laptop casings and mobile phone casings, mainly to meet the requirement of product portability.
Conclusion
The above are some of the differences between aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy. Different products can choose suitable materials for production according to specific requirements to achieve the desired functions and performance. Shine-Choose, as a professional die casting manufacturer, provides both aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy die casting solutions to help customers select the most appropriate material for their applications.