In a highly competitive market, the demand for aluminum alloy die-cast housings in electronic products, automotive parts, and industrial equipment is diverse and stringent. If you are designing or preparing to manufacture such housings, you face critical challenges such as combining precision and strength, customizing while controlling costs, and optimizing performance through material selection. This "Custom-made Aluminum Alloy Die cast Housings: A Comprehensive Guide" will analyze and answer these questions individually.
|
|
|
Currently, in the market, the minimum is approximately 0.5 centimeters, and the maximum is around 150 centimeters. The manufacturer's equipment determines the actual dimensions.
Design the draft angle.
For the housings of small-sized electronic products (such as mobile phones and tablets), the wall thickness is 0.8 - 1.5 millimeters; for the housings of small-sized electrical equipment (with a size ranging from a dozen centimeters to several dozen centimeters), the wall thickness is 1.5 - 2.5 millimeters; for the housings of medium-sized mechanical components and some automotive parts (with a size ranging from several dozen centimeters to one meter), the wall thickness is 2.5 - 4 millimeters; for the housings of large - sized industrial equipment, etc., the wall thickness is 4 - 8 millimeters or even thicker, which is determined explicitly according to the structural strength and load - bearing conditions.
The draft angle should be between 1° and 3°. If the draft angle is too small, the product may be scratched or die damaged during ejection.
It can make the housing more robust. Just like adding steel bars in building a house, ribs can increase the strength of the housing, making it less likely to be crushed or damaged by impact. Secondly, it can prevent the deformation of the aluminum alloy housing. If the housing is relatively thin, it is prone to bending or twisting, and ribs can help it maintain its shape.
The dimensional tolerance at the corners is relatively large, generally around ±0.2 mm to ±0.3 mm. The flatness tolerance can be controlled to a minimum of 0.05 mm to 0.1 mm. The dimensional tolerance at the edges is usually around ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm. The diameter tolerance of holes can generally be controlled at around ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm.
Try to avoid sharp corners as much as possible. Fillets can make the molten metal flow more smoothly, reducing defects such as flow marks and cold shuts. It is also convenient for demolding and reduces stress concentration.
Avoid undercut structures.
Design heat sinks, ventilation holes, and internal air ducts in the design.
The depth of recessed engraving for fonts can be around 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm. The height of raised fonts should not be too high, and generally, around 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm is more appropriate. The minimum size of fonts can be around 1.5 mm. The font lines should not be too thin; the minimum can be around 0.3 mm.
The following are the aluminum alloy material grades suitable for die casting:
Japanese standards: ADC12, ADC3
American standards: A360.0, A380.0, A383.0, A413.0
Chinese standard grades: YL112, YL113, YL302
Aluminum alloy materials with relatively good heat dissipation:
ADC12 has good fluidity and relatively high hardness, which can meet general heat dissipation requirements.
A380 has excellent fluidity, air-tightness, and heat-crack resistance and is suitable for manufacturing various heat-dissipating products.
YL113 has certain cost advantages and is suitable for manufacturing heat-dissipating products with relatively complex structures. It can meet the heat dissipation requirements of general industrial and civilian products.
|
|
|
Depending on your product, choosing a product decoration process suitable for your product can enhance the appearance grade of your product and also add some characteristics, such as waterproof, moisture-proof, and anti-oxidation. The following are some of the processes we commonly use.
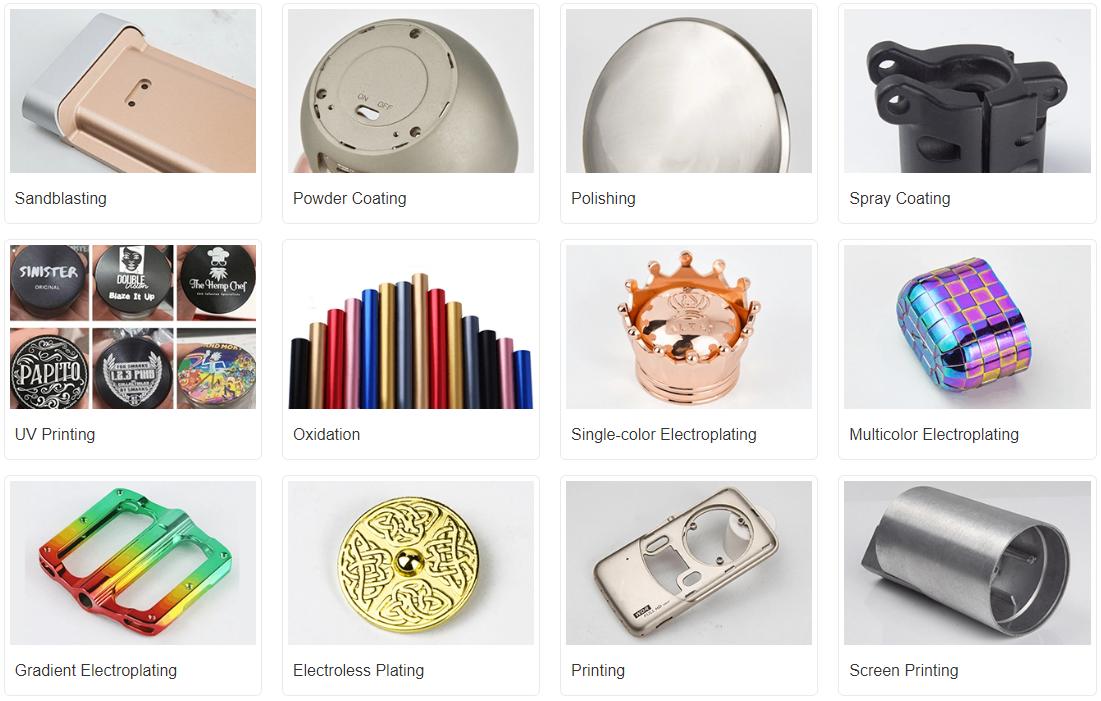
Anodizing: An oxide film is formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy by applying a high-voltage electric current.
Micro-arc oxidation: Under high voltage, micro-arc discharge is generated on the surface of the die-cast aluminum alloy to form a ceramic-like oxide film.
Powder spraying: The powder coating is electrostatically adsorbed and cured at high temperatures.
Electroplating process: A metal coating is deposited on the surface of aluminum alloy by the principle of electrolysis.
Electrophoretic process: The workpiece is used as an electrode and placed in an electrophoretic paint solution containing resin particles. Under the action of an electric field, the resin particles are deposited to form a coating.
Baking paint process: After pre-treatment, the paint is sprayed, and the paint surface is cured by high-temperature baking.
Sandblasting process: High-speed sand particles impact the surface of die-cast aluminum alloy, and the roughness is controlled by adjusting parameters.
Chemical passivation: The die-cast part is immersed in a chemical reagent solution to generate a passivation film.
Electroless plating: Without an external current, the reducing agent causes metal ions to be reduced and deposited on the surface of die-cast aluminum alloy to form a metal coating.
Nitriding treatment: Nitrogen atoms are made to penetrate the surface in a nitrogen-containing medium to form a nitride layer.
Chemical polishing: The workpiece is immersed in a polishing solution, and the microscopic protrusions are dissolved to make the surface bright and flat.
Mechanical polishing: Tools are used to remove flaws by friction, making the surface smooth and shiny.
Laser surface treatment: The surface of die-cast aluminum alloy is irradiated by a laser beam to change its properties.
Wire-drawing process: A wire-drawing wheel or belt rubs against the surface of the workpiece to form grooves.
How to choose a high - quality die-cast aluminum alloy housing manufacturer. Through the comprehensive evaluation of these critical factors, it can be ensured that the manufacturer can provide high-quality products and stable services.
1. Whether it has the ability of die development, the professionalism of the die design team, die-mining equipment, or processes. Examine the experience and ability of the die design team, as well as the precision and quality of die manufacturing.
2. The more die-casting machines, the better, and advanced die-casting equipment is preferred.
3. The number of production lines, the number of workers, and the number of production shifts. Understand whether the production capacity can meet the needs of large-volume orders, whether the delivery time is punctual, and whether it can respond to high requirements.
1.Quality Management System: Understand whether the manufacturer has established a sound quality management system, such as the ISO9001.
2. Testing Equipment and Methods: Find out whether the manufacturer is equipped with testing equipment such as a coordinate measuring machine, a metallographic analyzer, and a hardness tester and whether they conduct raw material testing, in-process testing, and finished product testing.
1. The longer a company has been established, the more experience it has and the more mature its technology is. 2. Understand the complexity of the products made in the manufacturer's factory or whether they have made housings similar to your products. 3. Find out whether the manufacturer has professional technical personnel who can provide technical consultations and solutions.
Before customizing aluminum die-cast housings, we must carefully consider every design detail, such as dimensions, shapes, wall thicknesses, etc., select suitable die-cast aluminum alloy materials and appropriate surface treatment processes, and then carefully choose high-quality manufacturers. Every step is indispensable. Mastering these key factors enables you to customize exclusive aluminum alloy housings, find reliable die-cast manufacturers, obtain high-quality products, and provide strong support for developing fields such as electronic products, automotive parts, and industrial equipment.
Copyright © 2023 :Guangdong Shine-Choose Smart Manufacturing Co., Ltd